As you guys can see below are the models illustrating bus, mux and merge blocks.
BUS:
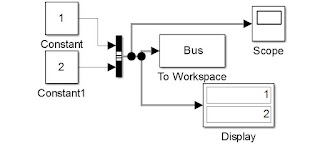
When two signals are fed to a bus, a bus signal is created. This bus signal can be configured using block parameters dialog box of box. Where one can rearrange the order of the signals or filter the signals if there are too many of them fed in.
Coming to the results of the above model
Scope:
Display block is already shown above.
To Workspace block: (Time series format)
You can see above that bus will form a struct variable in the workspace with number of fields equal to number of signals fed to it. Each of the field will be having time stamp and the signal value.
MUX:

As shown in the above model the mux is fed with 2 input signals and you notice that the display block is showing the same behavior as it is with the bus block.
Mux block will be multiplexing two or more scalar or vector signals and outputs a vector.

Above is the Mux block parameter dialog box.
Above is the scope for mux ouput which is exactly the same behavior as bus.

Output signal of the mux block shall be in double time series format (when to workspace block is set to time series format)
MERGE:

As above model suggests there should only be one active input signals to a merge block.
In the above first subsystem a constant block of value 1 is placed and in the second subsystem a constant block of value 2 is placed.
Generally the signals are fed from the conditional subsystems which are not enabled at once any instant.
Pulse generator block is configured as shown below.

Lets analyse the output of Merge block
Scope:

This shows that the merge block will only output a single signal.
Display block is already shown above.
To Workspace block will output

I hope the difference is clear now. Please provide your comments or doubts on the same.
Thanks!!





can you make a list of differences it would be better to glance at once
ReplyDeleteSure!!
ReplyDeletethere shall be an update for this post.
Much helpful! Thanks Sandeep...
ReplyDeleteVery helpful ! Thank you so much !
ReplyDeletethank you very much.
ReplyDelete